Fire insulation for floor drains

At a glance
Preventive fire insulation
The term for all organisational, constructional and technical measures designed to prevent the outbreak and spread of fires. This includes the compliant safeguarding of pipes and ceiling feedthroughs.
Fire insulating structural elements
Fire insulation elements fitted with a swelling agent (material which foams in case of fire) ensure that plastic pipes, drainage pipes and floor drains are safely sealed in the event of fire.
Fire resistance class/duration
The fire resistance class of a component provides information on how long it can withstand a fire. The classification is defined in the standards DIN 4102-2 and DIN EN 13501-2.
Installation of fire insulating structural elements
The low build height of the Dallmer fire insulation system provides the prerequisites that allow the drain pipe to be laid underneath the ceiling almost without clearance. In general the installation conditions required for approval, the type of drain, of pipeline and of the ceiling must be observed during installation.
Fire insulation in drainage technology

Fire insulation for floor drains and shower channels in concrete surfaces
Within the context of preventive fire insulation, plastic floor drains with a vertical outlet are regarded as pipe/ceiling feedthroughs that require sealing off. This is because if a fire breaks out, flames, smoke and heat can spread very quickly via the wastewater pipe and set fire to further floors of a building. In order to prevent this, it must be possible to professionally seal all feedthroughs of this type in compliance with the pertinent standards.
The same applies to flat roofs. In this case, the fire can jump to the roof via the roof drains. You will find more on the subject of fire insulation for roof drains here.
How the fire insulating structural element works
Dallmer offers fire insulating structural elements for sealing off floor feedthroughs that can be installed without the need for tools. The core piece of this element is a fire insulating insert made of an intumescent material (material that foams in the event of a fire) which begins to foam at a heat of approx. 150°C. The volume of the material increases approx. 15/20-fold. This seals off the ceiling feedthrough quickly, reliably and safely and prevents the spread of any heat, flames or smoke via this feedthrough.

1. The fire heats the material which foams in the event of a fire

2. Ceiling feedthrough is sealed off
Construction of fire insulating structural element

- Insert with grating
- Raising piece for bonded waterproofing according to DIN 18534
- Vertical drain body with outlet
- Sound insulation collar
- Mounting bracket and installation aid for tool-free assembly
- Fire and sound-insulating structural element
Fire resistance classes
DIN 4102-2 and DIN EN 13501-2
Fire insulating structural elements are divided into different fire resistance classes. This classification is regulated by the German standard DIN 4102-2 and the European standard DIN EN 13501-2. In both cases, the classification is determined by the length of time a component can withstand the fire.
| | DIN 4102-2 | DIN EN 13501-2 |
| These standards describe the fire resistance of a component or product using the following criteria | F = Fire resistance duration | R = Load capacity (Caution! Depending on the context, R may also stand for "pipe bushing") |
| Unit of measurement | Minutes – the value is always rounded down to the next multiple of 30 | Minutes |
| These are divided into the following classes | F 30/60/90 | REI 30/60/90/120 EI 30/60/90/120 |
Planners and architects must ensure that the fire resistance class of the selected fire insulating structural elements is appropriate for the roof where they are to be installed. Selecting a fire insulating element whose fire resistance class is too low will reduce the effectiveness of the ceiling fire resistance. Or in other words: a fire-resistant ceiling is of little use if the fire can spread via the piping. The following table shows which requirements the Model Building Code and the Regional Building Code have in relation to the fire resistance of floor drains in accordance with the building class:
Requirements relating to the fire resistance of floor drains according to the Model Building Code / Regional Building Code
| Building classes | GK 1 (a + b) | GK 2 | GK 3 | |
| OKF = Upper edge of common room flooring from upper edge of foundation |  Detached buildings <= 7 m OKF |  Buildings <= 7 m OKF |  Other buildings <= 7 m OKF | |
| Components in basements (ceilings), MBO § 31 (2) | 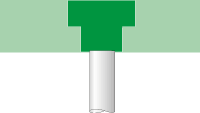 F 30 |  F 30 | 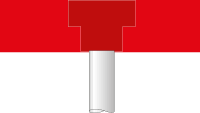 F 90 | |
| Components in upper floors (ceilings), MBO § 31 (1) |  F 30 |  F 30 |  F 30 | |
| Requirements for components on upper floors (ceilings) of "non-F 30 German federal states" prior to the introduction of the building regulation MBO 2002 |  F 30 |  F 30 |  F 30 | |
| Building classes | GK 4 | GK 5 | Special structures | |
| OKF = Upper edge of common room flooring from upper edge of foundation |  Buildings <= 13 m OKF |  Other buildings <= 22 m OKF |
regardless of height and high-rise buildings <= 22 m OKF | |
| Components in basements (ceilings), MBO § 31 (2) |  F 90 |  F 90 |  F 90 / F 120, 2) | |
| Components in upper floors (ceilings), MBO § 31 (1) |  F 60 / F 90, 3) |  F 90 |  F 90 | |
| Requirements for components on upper floors (ceilings) of "non-F 30 German federal states" prior to the introduction of the building regulation MBO 2002 |  F 60 / F 90, 3) |  F 90 |  F 90, 2) | |
- According to § 40 there are no provisions requiring the sealing-off of floor drains in apartments and building units smaller than 400 m 2 and with fewer than 2 floors (GK 1 (a+b)).
- Special structures are subject to different requirements. Details can be found in the special building regulations and special fire insulation concept, which form part of the building permit.
- As there are currently no bushings on the market for highly fire-retardant components, bushings for fire-resistant components must be installed.

Floor drains in F 30 components with sound and fire insulating requirements

Floor drains with sound insulation requirements

Floor drains in F 60 / F 90 / F 120 components with sound and fire insulating requirements
The required fire resistance durations for floor drains in the overview table must be taken into account during planning and implementation. Verification of the respective fire resistance duration must be provided in the form of a certification of suitability for use, e.g. a General Building Supervisory Authority Test Certificate (abP), a General Building Approval (abZ) or a General Design Certificate (aBG). This also applies to floor drains which are regulated in accordance with European standards and are documented in the Building Rules List.
"Floor drains are construction products which are regulated by European standards and therefore require no further approval for the function as a floor drain. As soon as floor drains contain mechanisms for preventive fire insulation, they require a General Building Approval (abZ) or a General Design Certificate (aBG). To adhere to the fire insulation objectives it is recommended that floor drains in R 30/60/90/120 quality be tendered. The client must submit a declaration of compliance for each floor drain type. For feedthroughs with an abZ/aBG, a type plate must be installed next to the floor drain on the underside of the ceiling." (Translation of quote from MLAR/LAR, 5th updated issue from authors Lippe, Czepuck, Möller, Reintsema)
Note
Adherence to the table will cover all previous and all new requirements. Verification of the respective fire resistance duration must be provided in the form of a certification of suitability for use, e.g. a General Building Supervisory Authority Test Certificate (abP), a General Building Approval (abZ) or a General Design Certificate (aBG).
Building areas with increased fire load
Underground car park according to Model Building Code
Yard and parking area drain 616 with fire insulation element 4
Installation of a floor drain with fire insulation element

Core drilling
Alternative: The appropriate polystyrene ceiling feedthrough

- Inserting fire insulation element
- The integrated installation aid (1) automatically seals the gap between the fire insulation element and the wall in the downwards direction
- Grouting spaces with MG II or MG III mortar

Installing floor drain with sound insulation collar ...

... and completing it
Note
A major benefit of the Dallmer fire insulation system is the low build height which means that the requirements for laying the drain lines underneath the ceiling almost without clearance are met.
Required for approved systems
Installation of floor drains with fire insulation pipe collars on the floor drain
Fire insulation collar installation instructions for floor drains on ceiling slab: installation instructions for sealing off combustible floor drains with R 30 to R 90 fire insulation collars underneath solid ceilings with requirements for the fire resistance duration. All variants for sealing off and examples (in relation to the pipe collars) must be implemented according to the specifications of the General Building Approval (abZ) or the General Design Certificate (aBG) for the respective R 30 to R 90 fire insulation collars. If necessary, "non-substantial deviations" (see diagram) from the abZ/aBG must be documented and confirmed by the owner of the approval. For substantial deviations from the abZ/aBG, applications must be made for approvals for individual circumstances or project-related design certificates (vBG).
Not approved!
Approved with restrictions!
Approved by the Deutsche Institut für Bautechnik (German Institute for Construction Engineering)!
Note on plastic drains with connection to combustible and non-combustible pipelines
Connecting pipes underneath the ceiling must be made up completely of a non-combustible pipe with non-combustible fastening as the loss of the room integrity cannot otherwise be avoided on the connecting pipe. This also applies to connections with ceiling feedthroughs. Transition pieces made of combustible building materials are permitted if the floor drains are engineered in R 30/60/90 quality.
Installation variant 1: Plastic drain with connection to NON-COMBUSTIBLE pipelines
Installation variant 2: Plastic drain with connection to COMBUSTIBLE pipelines
Application examples
Fire insulation for floor drains in F 30/60/90/120 components
Fire insulation with floor drains in existing buildings
Fire insulation for level-access showers with bonded waterproofing according to ZDB data sheet 1.2010 in existing buildings
Standards and directives
Model Building Code
Is published by the committee of ministers and senators of the 16 federal states responsible for urban development, construction housing (ARGEBAU).
Model Conduit Systems Directive, issued by the ARGEBAU, published by the German Institute for Construction Engineering (DIBt)
The MLAR explains how to achieve the (fire) safety targets specified by the Model Building Code. It serves as a guideline for the planning and installation of conduits and drains in terms of preventative fire insulation. The LAR is the issue announced as construction legislation in the respective federal state. The LAR describes the requirements of conduits, including fastenings and insulating materials, in conjunction with installation in emergency escape routes. The LAR aims to improve preventative fire insulation in conduit systems and help all involved to erect buildings to an appropriate and compatible safety standard. The LAR defines the execution principles for the penetration of a vertical pipe or a floor/roof drain through a fire-resistant wall or ceiling. The wall and/or ceiling feedthroughs then have to be implemented in conjunction with national certification of suitability for use (abZ/abP/aBG) in R 30/60/90/120 quality.
This standard refers to gravity drainage within buildings and specifications, including how drainage systems are to be planned and installed in order to ensure reliable protection against the spreading of fires. In buildings where pipes need to be fed through walls and ceilings that are subject to special requirements in terms of fire resistance, special measures are required according to national and international regulations.
This standard refers to the fire behaviour of components and materials. It defines the fire resistance classes of materials to be used in house technology and how the components and materials are to be tested.
European standard for the fire behaviour classification of building products and building elements. It serves a similar purpose at European level to DIN 4102 at German level.
Glossary
Fire insulation includes all measures that contribute towards the prevention and control of fires. Because this is a broad and complex field, different types of fire insulation are divided into the following categories:
- Preventive fire insulation
Concrete measures that contribute towards enabling a fire to be extinguished as quickly as possible and that help save people and animals. - Technical fire insulation
All technical systems that help fire prevention, fire detection and fire suppression – typical examples are smoke detectors, automatic extinguishing systems and smoke and heat extraction systems. - Structural fire insulation
This specifies the materials and components that may be used and how emergency escape routes and extinguishing systems are to be planned. - Organisational fire insulation
Fire officers and company training on the topic of fire insulation fall under the heading of organisational fire insulation. - Defensive fire insulation
All concrete measures aimed at preventing fires and stopping the spread of fires.
Anhand der DIN 4102 oder der DIN EN 13501 werden Bauprodukte in verschiedene Klassen eingeteilt, abhängig davon, wie lange sie ihre Funktionsfähigkeit unter Hitzeeinwirkung behalten.
Relevant products
Dated: November 2020




























